Published: 01 March 2024
Views: 563
March Tip of the Month
Positive Pressure Ventilation
Any patient that needs respiratory support with positive pressure ventilation (PPV) requires the use of a bag valve mask (BVM). In order to ensure this intervention is successful, NWRPCP recommends the following steps:
- Optimize patient positioning by placing them in the sniffing position to align the three anatomic axes: oral axis, pharyngeal axis, and laryngeal axis (see image below). This will ensure the flow of oxygen follows the path of least resistance.
- Utilize two person mask seal when resources are available
- Consider using ‘MR. SOPA’ to improve ventilations
- Mask - consider lifting the face into the mask rather then pressing the mask into the face to achieve an appropriate seal. In addition, consider changing the size of the mask if applicable.
- Reposition - reposition the head to open the airway; consider the sniffing position
- Suction - suction the oral phayrnx
- Open the airway - consider airway adjuncts: OPA and/or NPA
- PEEP - not applicable to PCP/ACP scope of practice
- Advanced Airway - consider using advanced airways; SGA and/or ETT
- Apply EtCO2 monitoring
- Confirm ventilations are achieved by auscultating
- Document accordingly
A: Incorrect position B: Sniffing Position
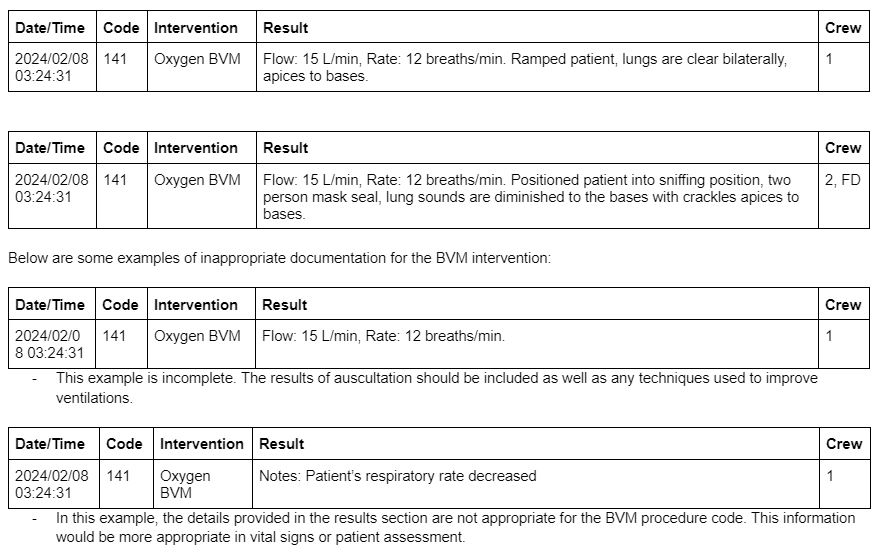
The following are examples of appropriate documentation when using a BVM:
When documenting the result of a BVM intervention, be sure to include the flow rate, breathing rate, and the results of auscultation and any techniques or maneuvers used to enhance ventilations.
Previous Tips
-
March Tip of the Month - Seizures: When Treatment Ends on Scene
-
February Tip of the Month - Owning the Outcome: Ethics, Failure, and Legal Responsibility
-
January Tip of the Month - Mean Arterial Pressure "MAP" - The Rule of 65
-
**AMENDED** Winter Emergencies: Recognition and Care for Hypothermia and Frostbite
-
November Tip of the Month - Not "Just" the Flu: Recognizing High-Risk Respiratory Illness
-
October Tip of the Month - Diabetic Emergencies
-
September Tip of the Month - Sepsis
-
August Tip of the Month - Mass Casualty Incidents
-
July Tip of the Month - Breaking down Burns
-
June tip of the month - High-Quality CPR & Defibrillation